Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is a post-translational modification carried out by members of de poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) family. These polymers are involved in various cellular processes including DNA damage signaling and repair, cell cycle regulation, cell differentiation and cell death pathways. This modification is transient, being poly(ADP-ribose)glycohydrolase the main degrading enzyme.
The parasites Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei bear only one copy of these enzymes, differing from other organisms. These enzymes also have different localization and activity requirements than those described for their mammalian counterparts. These pose them as putative therapeutic targets, encouraging the search for inhibitors of this pathway that are specific for these trypanosomatids.
Lab Members
Ph. D. Salomé Vilchez Larrea
Investigador Asistente CONICET
vilchez.ingebi@gmail.com
Lic. Maria Laura Kevorkian
Becaria Doctoral CONICET
laurakevorkian@gmail.com
Publications
Schlesinger M, Vilchez Larrea SC, Haikarainen T, Narwal M, Venkannagari H, Flawia MM, Lehtiö L, Fernández Villamil SH.
Parasites and Vectors. (2016) 9:173. DOI 10.1186/s13071-016-1461-1 marzo 2016.
VERO cells harbor a poly-ADP-ribose belt partnering their epithelial adhesion Belt. Lafon Hughes L, Vilchez Larrea SC, Kun A, Fernández Villamil SH. 1.
PeerJ 2:e617 http://dx.doi.org/10.7717/peerj.617 oct 2014.
Host Cell Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase Is Crucial for Trypanosoma cruzi Infection Cycle. Vilchez Larrea SC, M, Schlesinger M, Kevorkian ML, Flawia MM, Alonso GD, Fernández Villamil SH.
PLoS ONE, vol 8 issue 6, 2013.
The metabolism of 9-chloro-β-lapachone and its effects in isolated hepatocytes. The involvement of NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). Fernández Villamil SH, Carrizo P, Di Rosso E, Molina Portela MP and Dubin M.
Chem Biol Interact. 200(2-3):84-91, 2012.
Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase interferes with Trypanosoma cruzi infection and proliferation of the parasite.
Vilchez Larrea SC, Haikarainen T, Narwal M, Schlesinger M, Venkannagari H, Flawia MM, Fernández Villamil SH, Lehtiö L.
PLoS ONE, vol 7 issue 9, 2012.
Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase plays a diffrential role in DNA damage response and cell death pathways in Trypanosoma cruzi.
Vilchez Larrea SC, Alonso GD, Schlesinger M, Torres HN, Flawiá MM and Fernández Villamil SH.
International Journal for Parasitology, 41: 405-416, 2011.
Metabolism of Poly-ADP-ribose in Trypanosomatids.
Alonso GD, Vilchez Larrea SC and Fernández Villamil SH.
Parasitology Research Trends. Ed: Olivier De Bruyn and Stephane Peeters. 6: 1-11, 2010.
TcPARP: A DNA damage-dependent poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase from Trypanosoma cruzi. Fernández Villamil SH, Baltanás R, Alonso GD, Vilchez Larrea SC, Torres HN, Flawiá MM.
International Journal for Parasitology, 38: 277–287, 2008.
Research Lines
Structural and metabolic studies of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) and poly(ADP-ribose)glycohydrolase (PARG) enzymes from T. cruzi and T brucei
One of our working subjects is the study of PARP and PARG and the role of poly(ADP-ribose) on cell cycle, DNA damage response and immune system evasion in the different forms of these parasites.
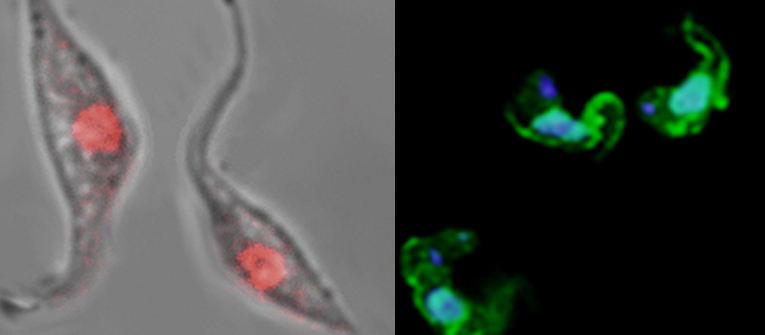
Nuclear PAR generated by genotoxic stress in T. cruzi epimastigotes and blood stream form of Trypanosoma brucei
Role of polymers of ADP-ribose during the host cell response elicited by T. cruzi infection
A new focus has been placed on unravelling the participation of ADP-ribose polymer metabolism in the host cell during the infection process and the immflamatory response mediated by PAR.
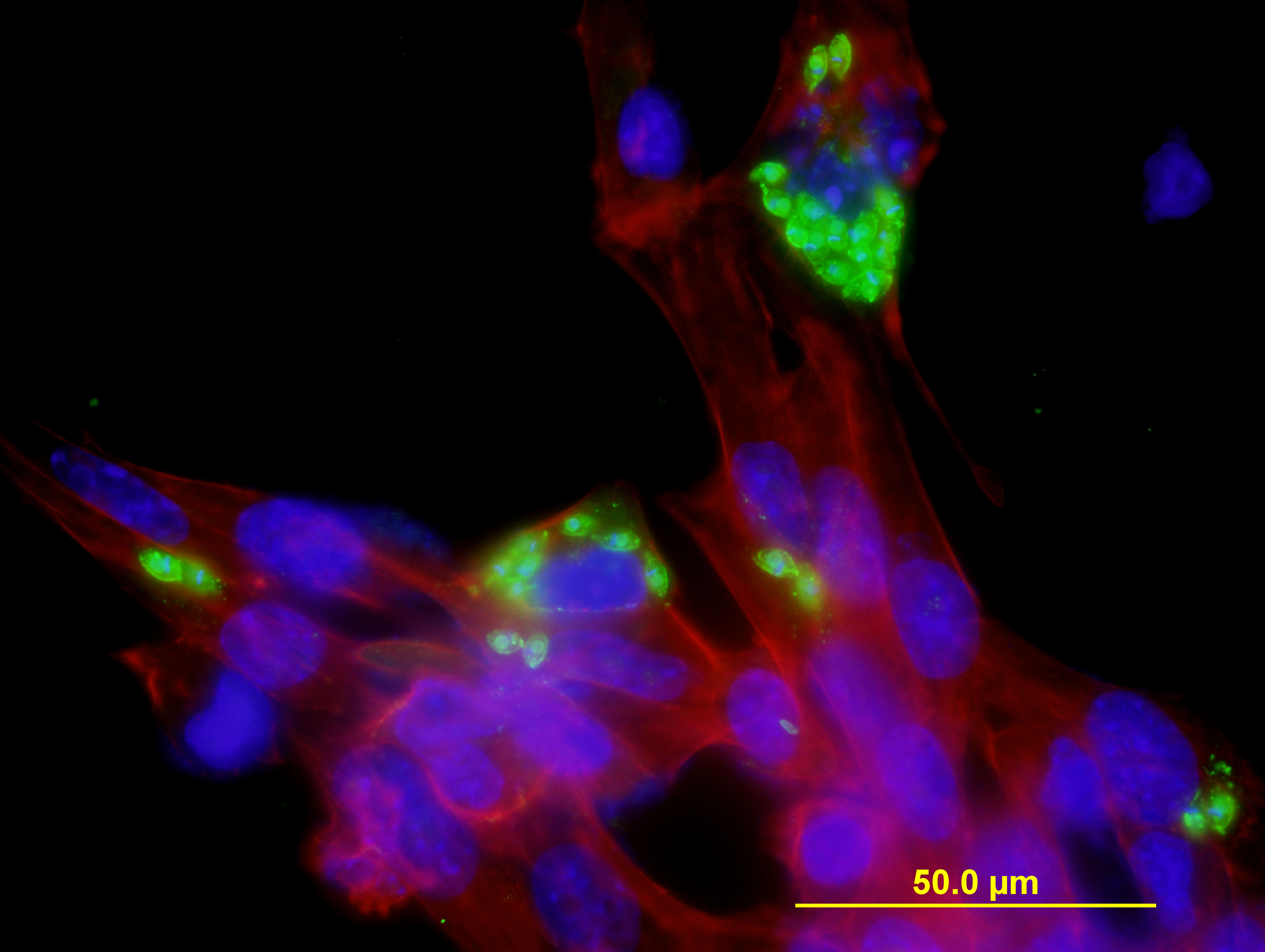
Trypanosoma cruzi amastigotes in HL-1 cells
Membrane associated ADP-ribose polymers and their role during T. cruzi invasion
We seek to study PAR metabolism associated with intercellular junctions and deciphering which PARPs might be involved and their possible targets, focusing on the dynamics triggered by T cruzi invasión.
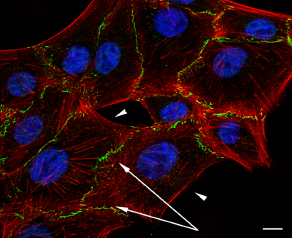
Vero cells: actin microfilaments (red), PAR (green) in epithelial adhesion belt
Ex Lab Members
Dra. Dolores Podesta
Dr. Rodrigo Baltanas
Dra. Patricia Caicedo Burbano
Dra. Mariana Schlesingher

Ph.D Silvia Fernández Villamil
- Biochemist. School of Pharmacy and Biochemistry University of Buenos Aires, Argentine.
- PhD in Biochemistry. University of Buenos Aires, Argentine.
- Member of the Research Career in the National Research Council of Argentina (CONICET): Rank 3 of 5.
- Assistant Professor, Department of Biological Chemistry. School of Pharmacy and Biochemistry. University of Buenos Aires.
- Member of the Argentinean Society of Biochemist Research and Molecular Biology.Member of the Argentinean Society of Protozoology.
